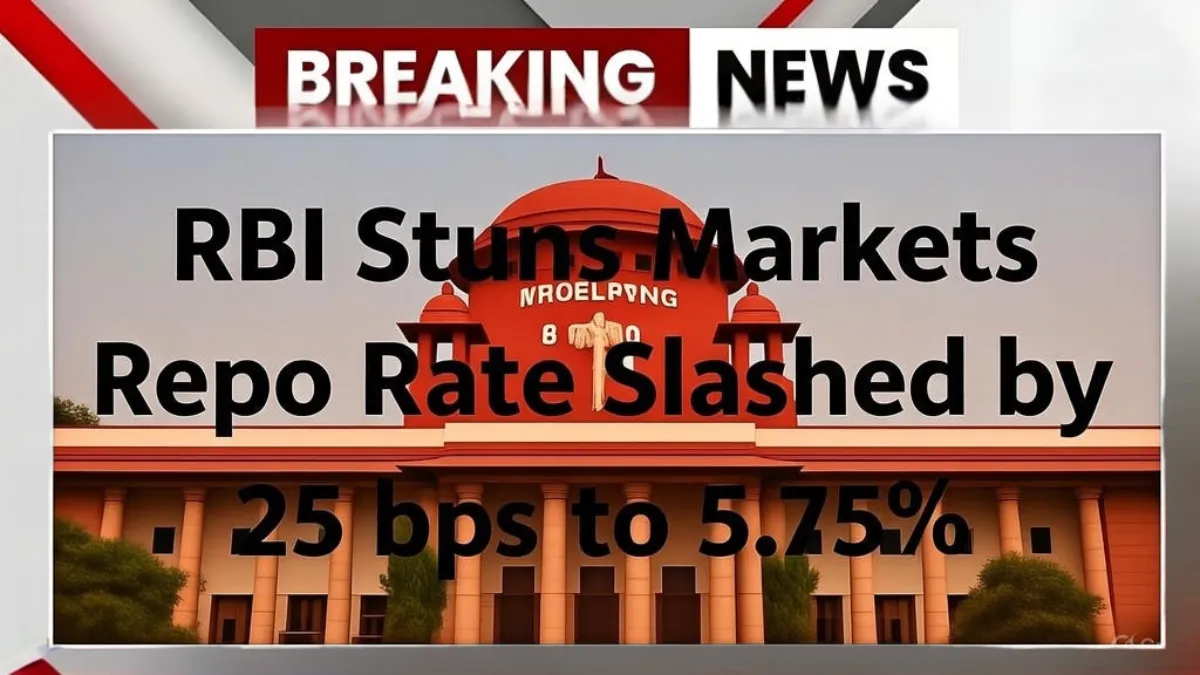
In a move that caught markets by surprise, the Reserve Bank of India has reduced the repo rate by 25 basis points, bringing it down to 5.75 percent. Along with the rate cut, the central bank has shifted its policy stance to “accommodative,” clearly signalling its intent to support economic growth through easier monetary conditions. The decision is expected to have wide-ranging implications for borrowers, savers, businesses, and financial markets.
The rate cut comes amid moderating inflation pressures and concerns over slowing economic momentum. By lowering the cost at which banks borrow from the RBI, the central bank aims to encourage lending, boost consumption, and revive investment activity across sectors.
What the Repo Rate Cut Means
The repo rate is the key interest rate at which commercial banks borrow short-term funds from the RBI. A reduction in this rate lowers the overall cost of funds for banks, enabling them to pass on the benefit to customers through reduced loan interest rates. Home loans, personal loans, auto loans, and business credit are likely to become more affordable in the coming months if banks transmit the cut effectively.
Why RBI Changed Its Policy Stance
The shift to an accommodative stance indicates that the RBI is now more focused on supporting economic growth rather than tightening liquidity. This stance allows room for further rate cuts or supportive measures if economic conditions demand it. The central bank appears confident that inflation is under control and that growth needs immediate policy support.
| Policy Indicator | Before Decision | After Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Repo Rate | 6.00 percent | 5.75 percent |
| Policy Stance | Neutral | Accommodative |
| Objective | Inflation control | Growth support |
| Impact Area | Credit conditions | Cheaper borrowing |
Impact on Borrowers
Borrowers stand to gain the most from the rate cut. Existing loans linked to external benchmarks may see quicker reductions in interest rates, lowering monthly EMIs. New borrowers could also benefit from more attractive loan offers as banks compete to expand their credit portfolios.
Effect on Fixed Deposits and Savers
While borrowers benefit, depositors may face lower returns on fixed deposits and savings instruments over time. Banks often adjust deposit rates downward following repo rate cuts, which could impact individuals relying on interest income, particularly senior citizens.
Market Reaction and Economic Outlook
Financial markets typically respond positively to rate cuts, as lower interest rates improve liquidity and corporate profitability. The accommodative stance also reassures investors that the RBI is prepared to act proactively to sustain economic momentum. Over the medium term, the decision is expected to support consumption, housing demand, and business expansion.
What to Expect Going Forward
With the policy stance now accommodative, future monetary policy decisions will closely track inflation trends, global economic conditions, and domestic growth indicators. If inflation remains within comfort levels, further supportive measures cannot be ruled out.
Conclusion: The RBI’s decision to cut the repo rate to 5.75 percent and adopt an accommodative stance marks a clear shift toward growth support. Lower borrowing costs and easier credit conditions could provide a timely boost to the economy if banks transmit the benefits effectively.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and reflects policy announcements and general economic analysis. Actual interest rate transmission, loan rates, and market impact may vary based on banking practices and future RBI decisions.